Preserving and Resetting State
State is isolated between components. React keeps track of which state belongs to which component based on their place in the UI tree. You can control when to preserve state and when to reset it between re-renders.
Þú munt læra
- How React “sees” component structures
- When React chooses to preserve or reset the state
- How to force React to reset component’s state
- How keys and types affect whether the state is preserved
The UI tree
Browsers use many tree structures to model UI. The DOM represents HTML elements, the CSSOM does the same for CSS. There’s even an Accessibility tree!
React also uses tree structures to manage and model the UI you make. React makes UI trees from your JSX. Then React DOM updates the browser DOM elements to match that UI tree. (React Native translates these trees into elements specific to mobile platforms.)
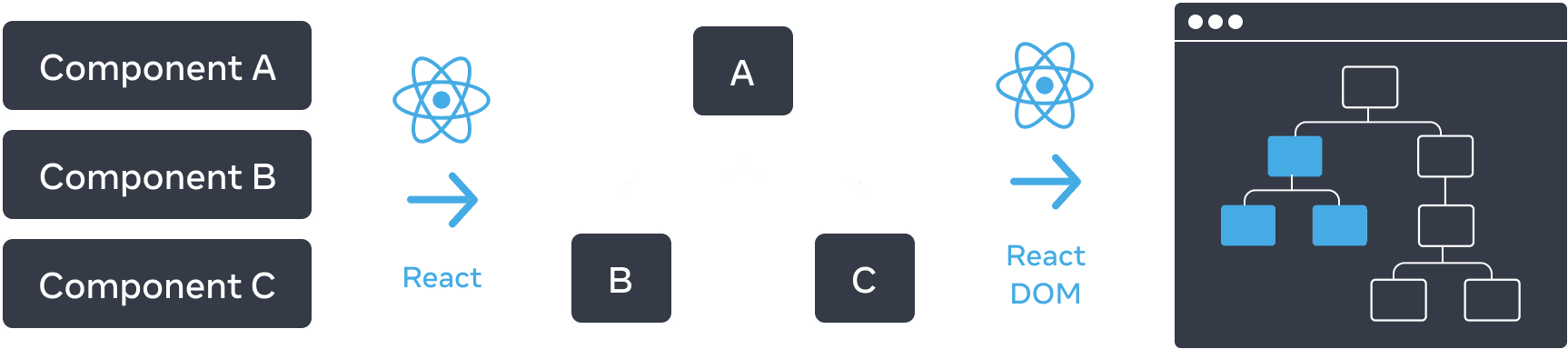
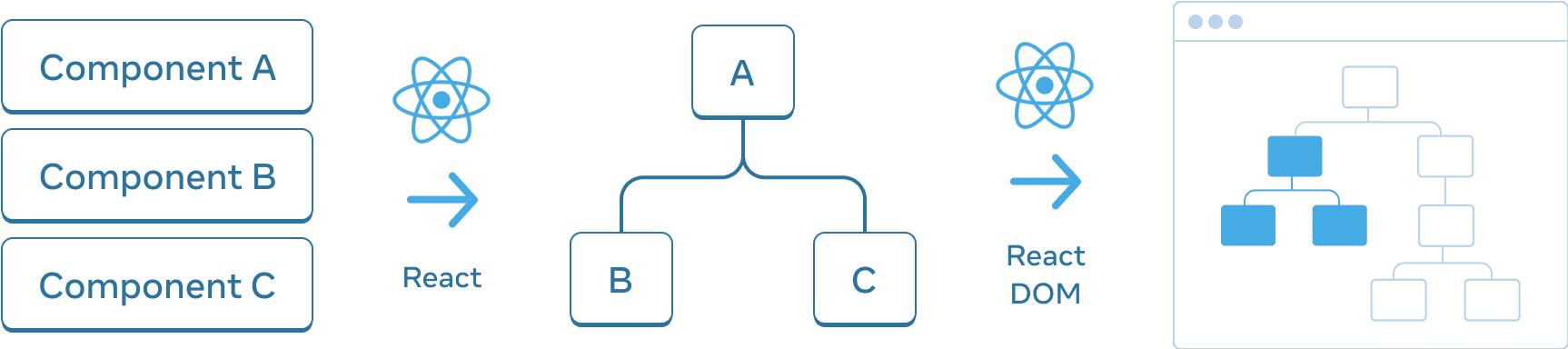
From components, React creates a UI tree which React DOM uses to render the DOM
State is tied to a position in the tree
When you give a component state, you might think the state “lives” inside the component. But the state is actually held inside React. React associates each piece of state it’s holding with the correct component by where that component sits in the UI tree.
Here, there is only one <Counter /> JSX tag, but it’s rendered at two different positions:
import { useState } from 'react'; export default function App() { const counter = <Counter />; return ( <div> {counter} {counter} </div> ); } function Counter() { const [score, setScore] = useState(0); const [hover, setHover] = useState(false); let className = 'counter'; if (hover) { className += ' hover'; } return ( <div className={className} onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)} onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)} > <h1>{score}</h1> <button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}> Add one </button> </div> ); }
Here’s how these look as a tree:
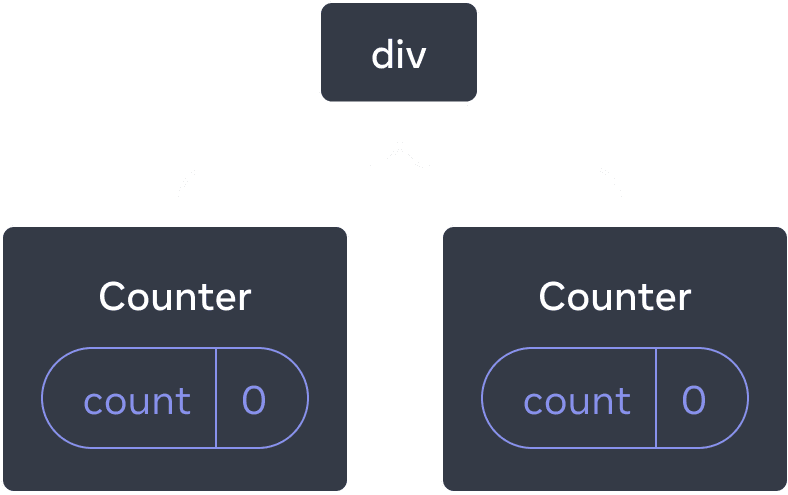
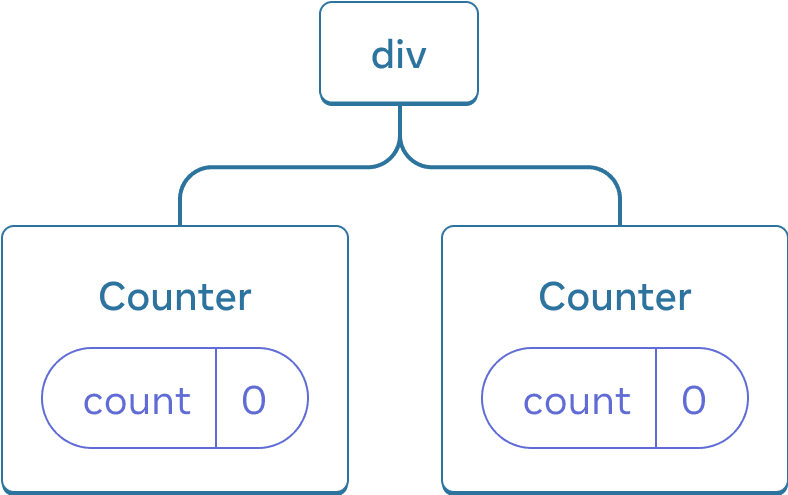
React tree
These are two separate counters because each is rendered at its own position in the tree. You don’t usually have to think about these positions to use React, but it can be useful to understand how it works.
In React, each component on the screen has fully isolated state. For example, if you render two Counter components side by side, each of them will get its own, independent, score and hover states.
Try clicking both counters and notice they don’t affect each other:
import { useState } from 'react'; export default function App() { return ( <div> <Counter /> <Counter /> </div> ); } function Counter() { const [score, setScore] = useState(0); const [hover, setHover] = useState(false); let className = 'counter'; if (hover) { className += ' hover'; } return ( <div className={className} onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)} onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)} > <h1>{score}</h1> <button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}> Add one </button> </div> ); }
As you can see, when one counter is updated, only the state for that component is updated:
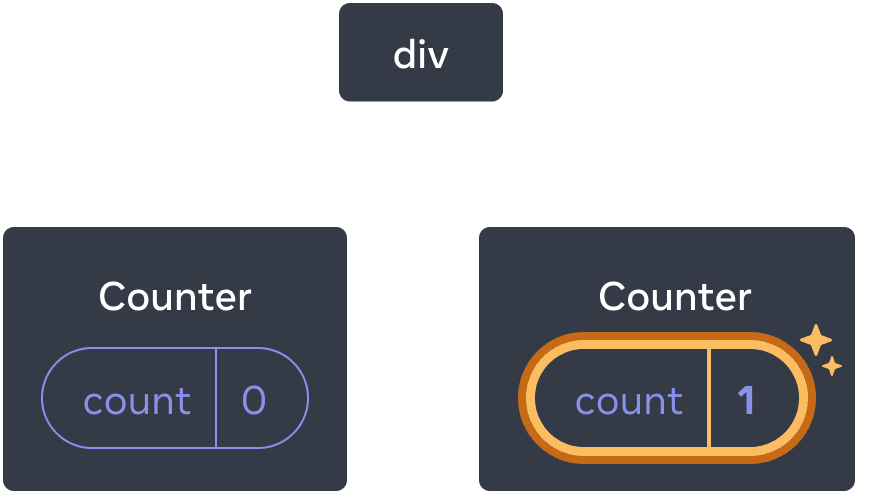
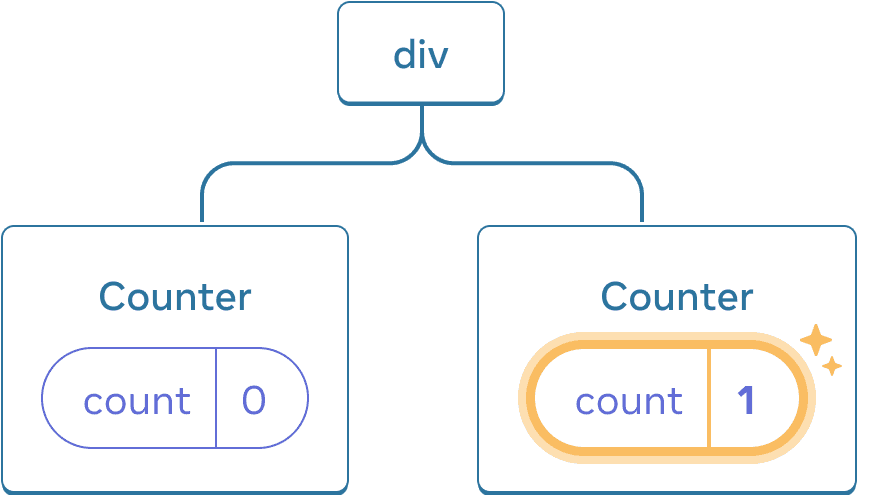
Updating state
React will keep the state around for as long as you render the same component at the same position. To see this, increment both counters, then remove the second component by unchecking “Render the second counter” checkbox, and then add it back by ticking it again:
import { useState } from 'react'; export default function App() { const [showB, setShowB] = useState(true); return ( <div> <Counter /> {showB && <Counter />} <label> <input type="checkbox" checked={showB} onChange={e => { setShowB(e.target.checked) }} /> Render the second counter </label> </div> ); } function Counter() { const [score, setScore] = useState(0); const [hover, setHover] = useState(false); let className = 'counter'; if (hover) { className += ' hover'; } return ( <div className={className} onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)} onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)} > <h1>{score}</h1> <button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}> Add one </button> </div> ); }
Notice how the moment you stop rendering the second counter, its state disappears completely. That’s because when React removes a component, it destroys its state.
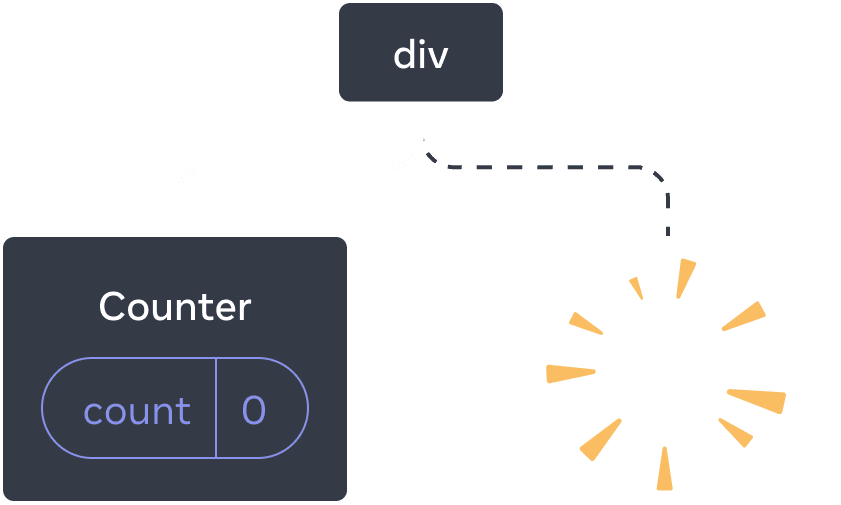
Deleting a component
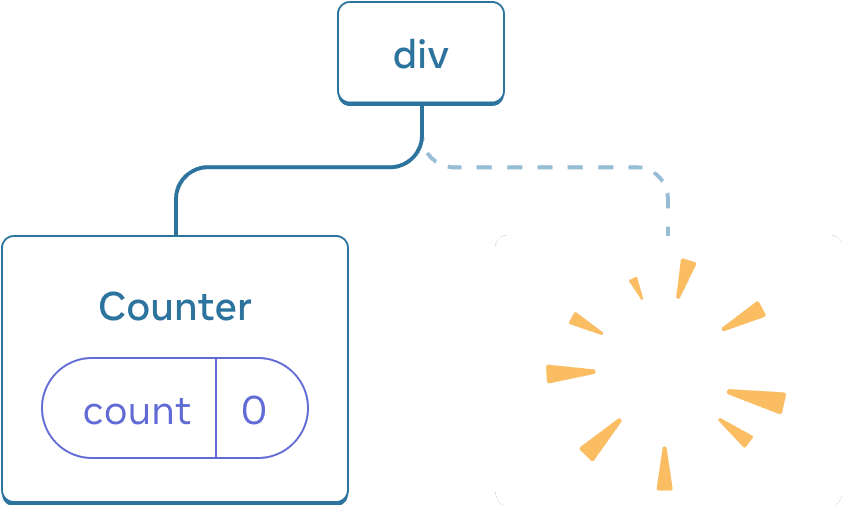
When you tick “Render the second counter”, a second Counter and its state are initialized from scratch (score = 0) and added to the DOM.
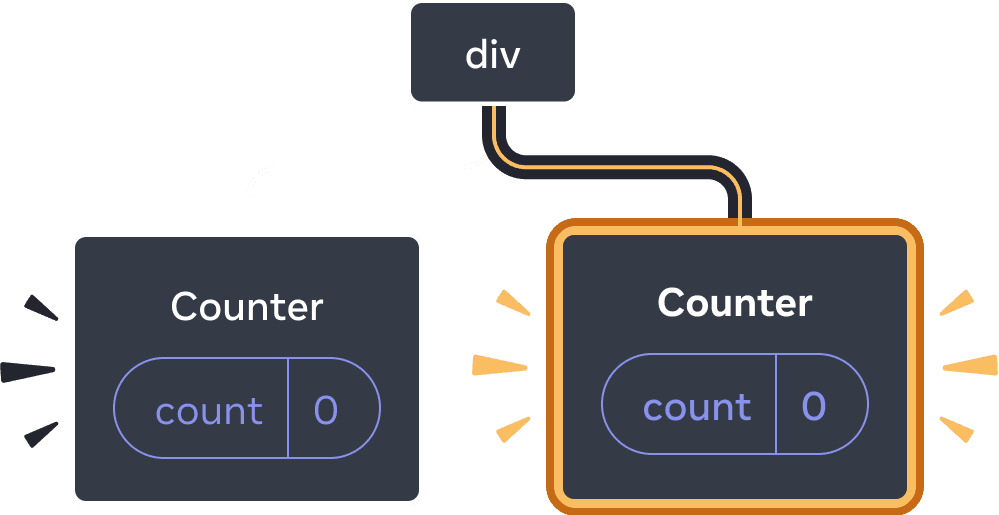
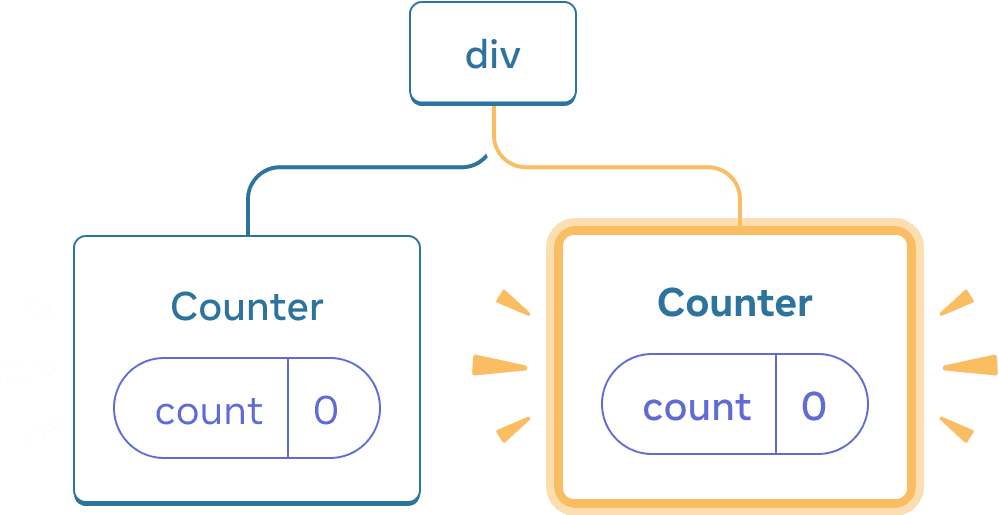
Adding a component
React preserves a component’s state for as long as it’s being rendered at its position in the UI tree. If it gets removed, or a different component gets rendered at the same position, React discards its state.
Same component at the same position preserves state
In this example, there are two different <Counter /> tags:
import { useState } from 'react'; export default function App() { const [isFancy, setIsFancy] = useState(false); return ( <div> {isFancy ? ( <Counter isFancy={true} /> ) : ( <Counter isFancy={false} /> )} <label> <input type="checkbox" checked={isFancy} onChange={e => { setIsFancy(e.target.checked) }} /> Use fancy styling </label> </div> ); } function Counter({ isFancy }) { const [score, setScore] = useState(0); const [hover, setHover] = useState(false); let className = 'counter'; if (hover) { className += ' hover'; } if (isFancy) { className += ' fancy'; } return ( <div className={className} onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)} onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)} > <h1>{score}</h1> <button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}> Add one </button> </div> ); }
When you tick or clear the checkbox, the counter state does not get reset. Whether isFancy is true or false, you always have a <Counter /> as the first child of the div returned from the root App component:
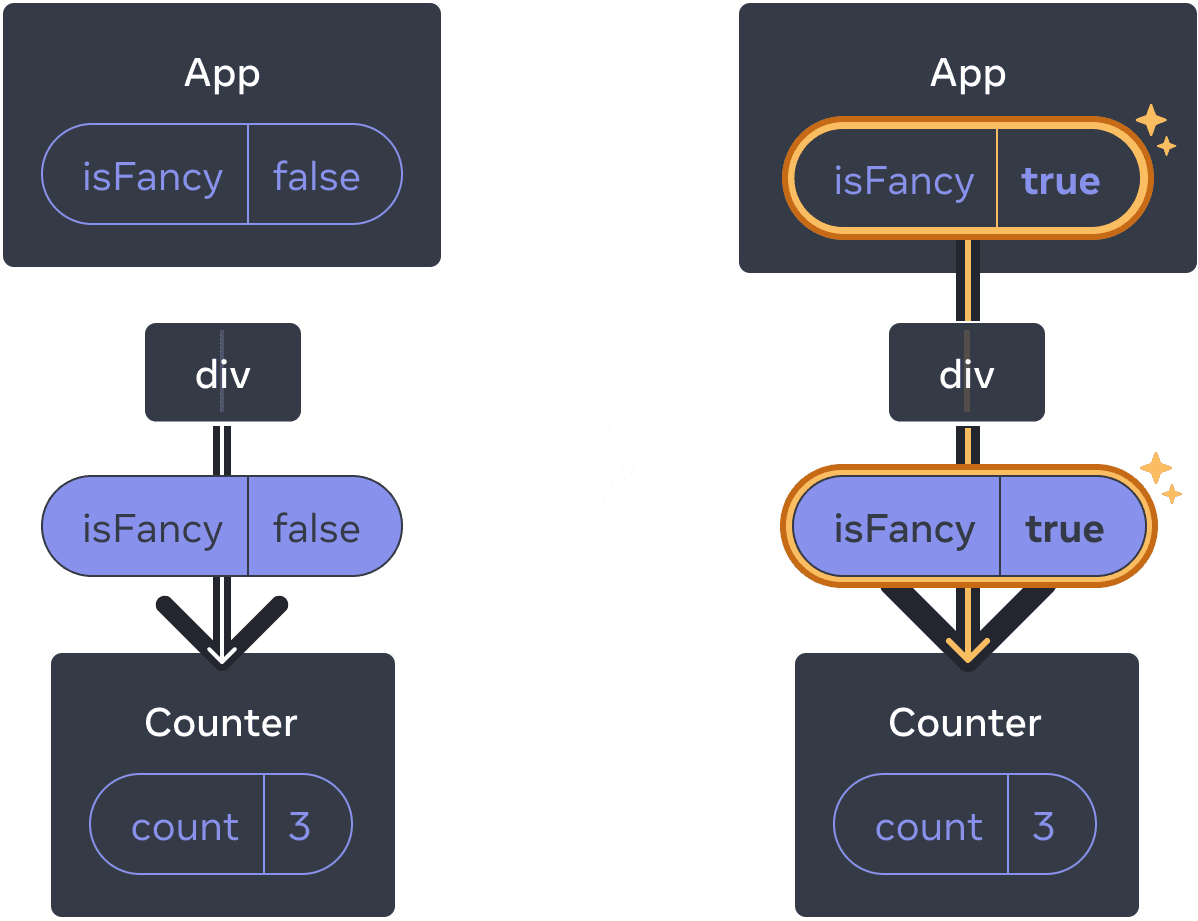
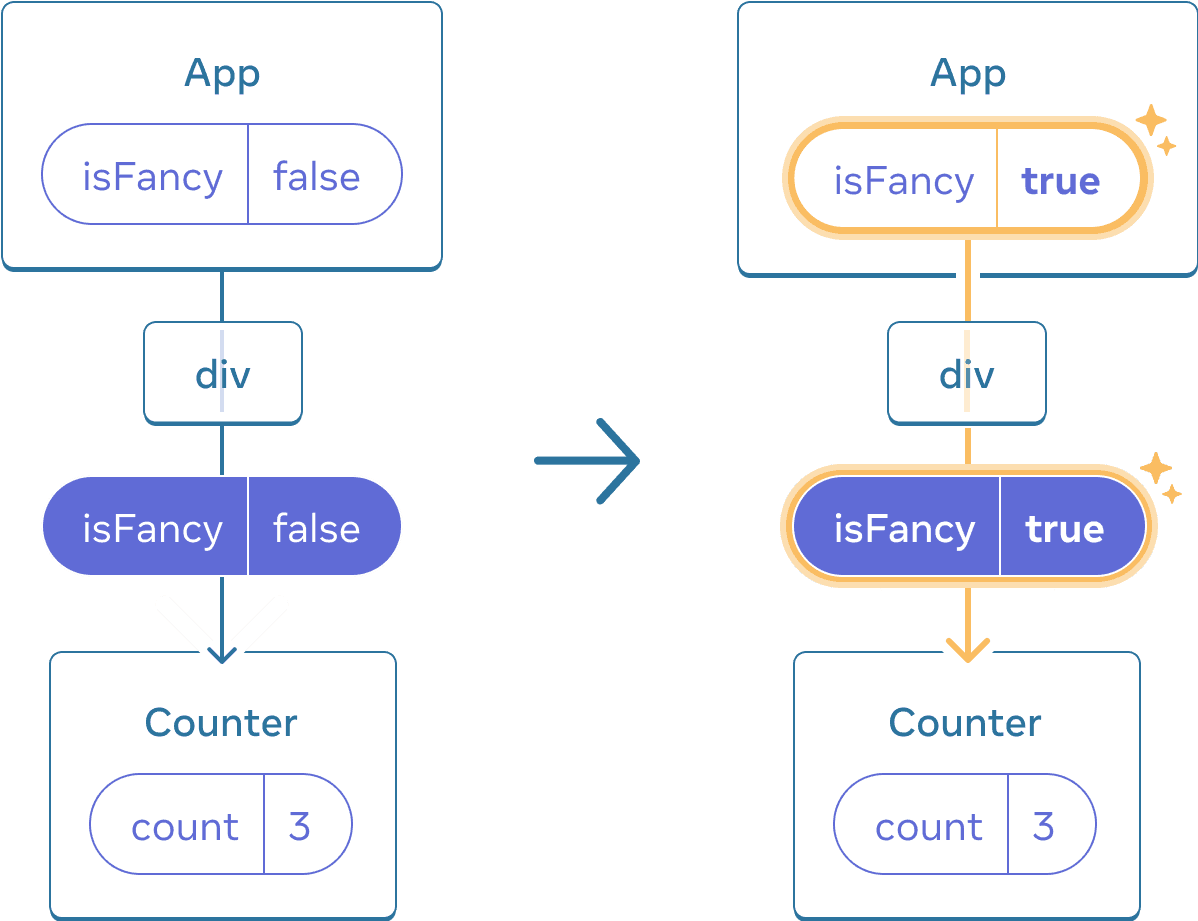
Updating the App state does not reset the Counter because Counter stays in the same position
It’s the same component at the same position, so from React’s perspective, it’s the same counter.
Different components at the same position reset state
In this example, ticking the checkbox will replace <Counter> with a <p>:
import { useState } from 'react'; export default function App() { const [isPaused, setIsPaused] = useState(false); return ( <div> {isPaused ? ( <p>See you later!</p> ) : ( <Counter /> )} <label> <input type="checkbox" checked={isPaused} onChange={e => { setIsPaused(e.target.checked) }} /> Take a break </label> </div> ); } function Counter() { const [score, setScore] = useState(0); const [hover, setHover] = useState(false); let className = 'counter'; if (hover) { className += ' hover'; } return ( <div className={className} onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)} onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)} > <h1>{score}</h1> <button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}> Add one </button> </div> ); }
Here, you switch between different component types at the same position. Initially, the first child of the <div> contained a Counter. But when you swapped in a p, React removed the Counter from the UI tree and destroyed its state.
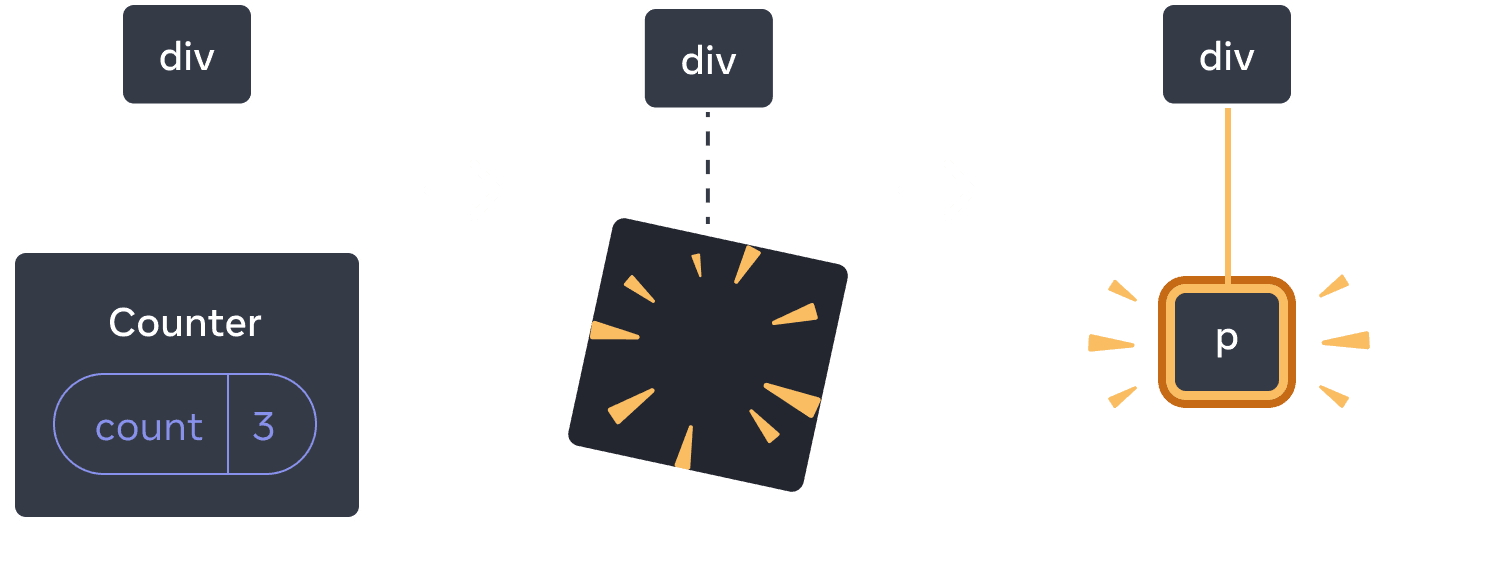
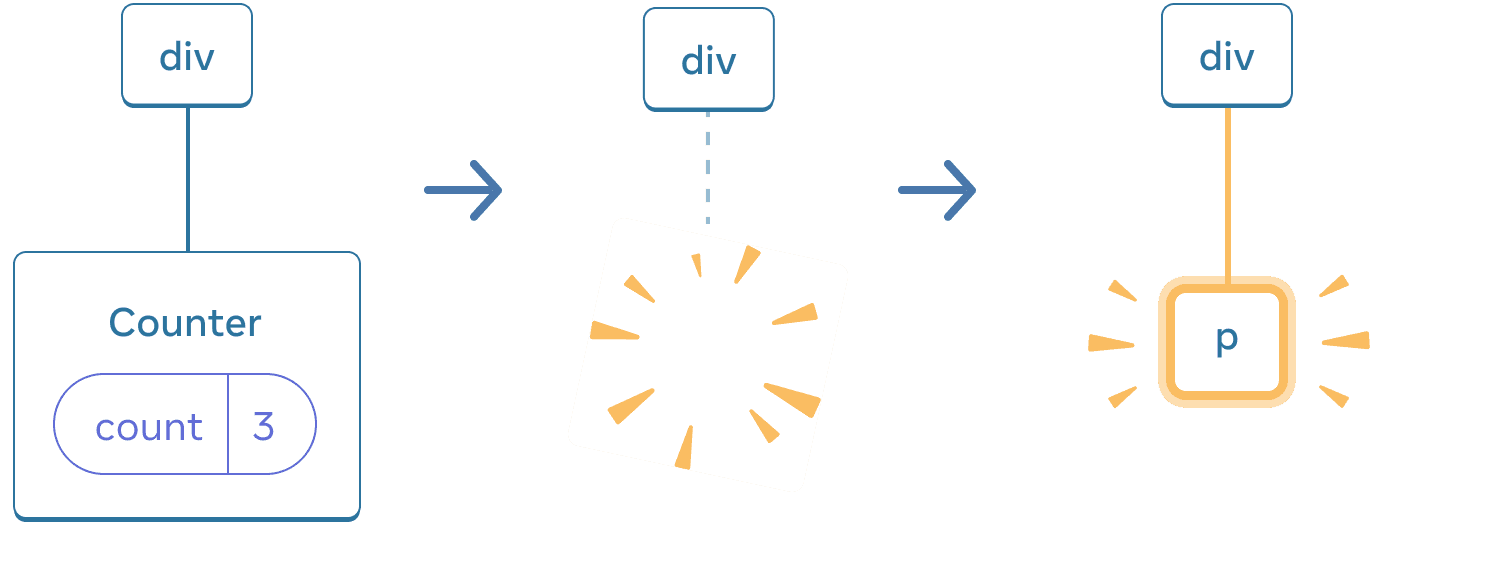
When Counter changes to p, the Counter is deleted and the p is added
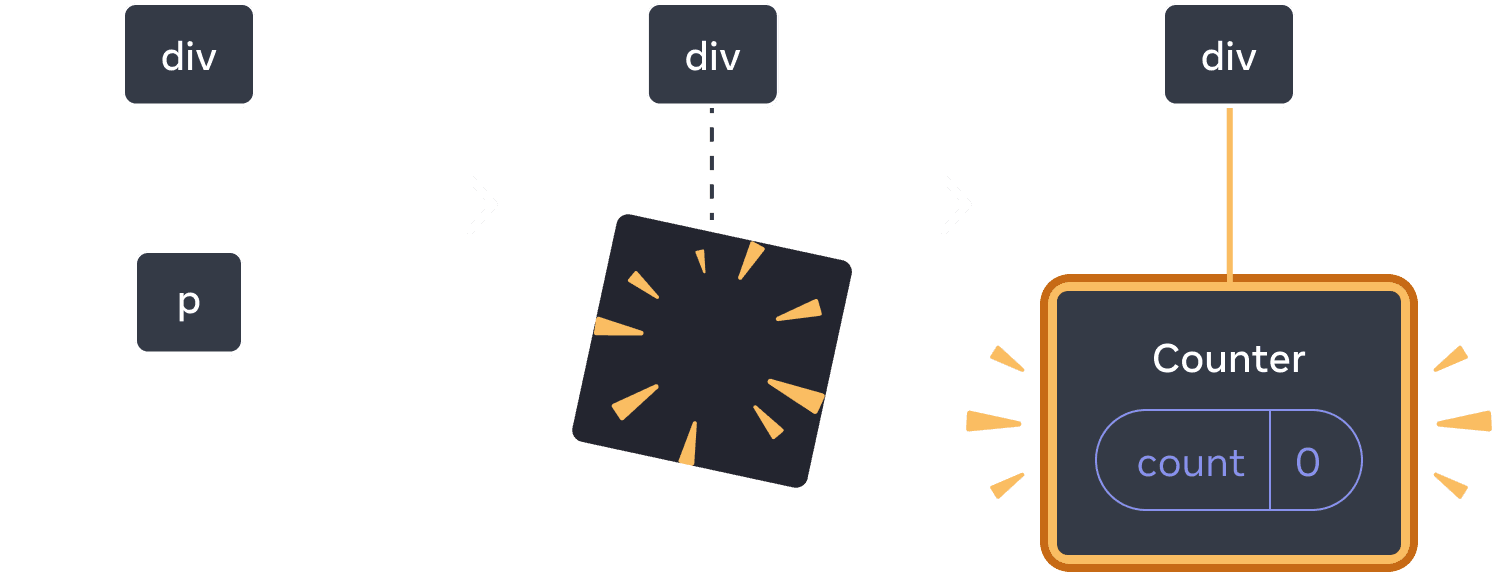
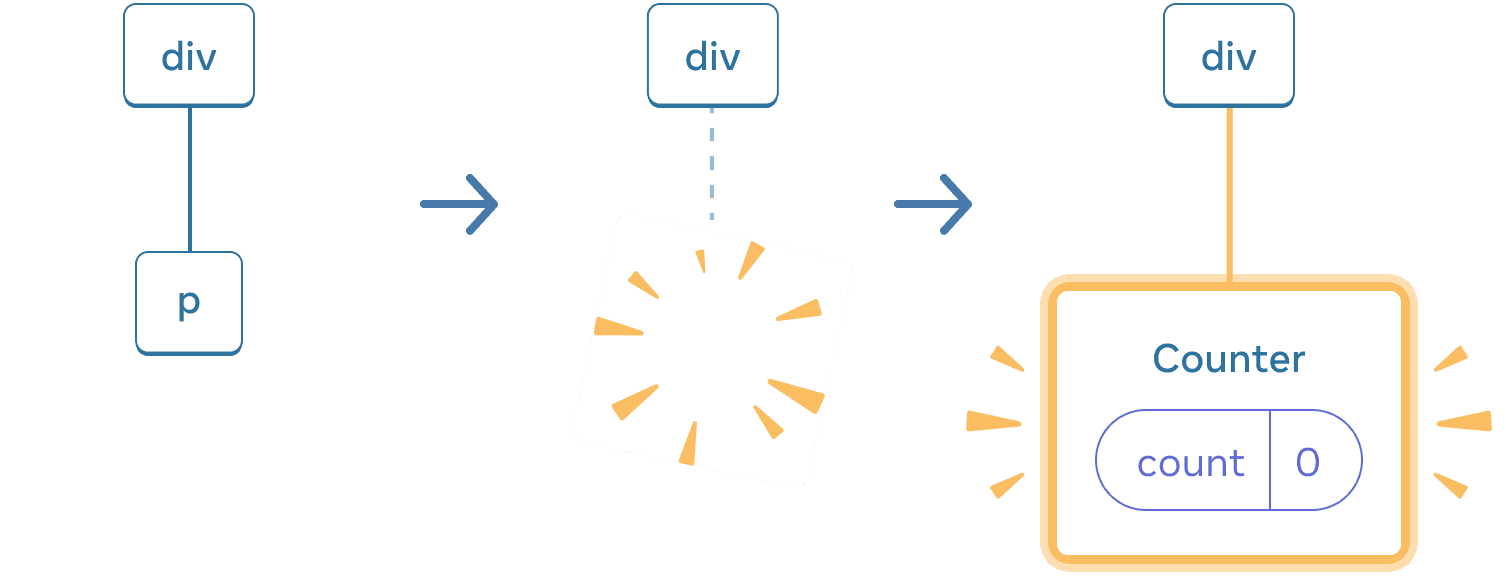
When switching back, the p is deleted and the Counter is added
Also, when you render a different component in the same position, it resets the state of its entire subtree. To see how this works, increment the counter and then tick the checkbox:
import { useState } from 'react'; export default function App() { const [isFancy, setIsFancy] = useState(false); return ( <div> {isFancy ? ( <div> <Counter isFancy={true} /> </div> ) : ( <section> <Counter isFancy={false} /> </section> )} <label> <input type="checkbox" checked={isFancy} onChange={e => { setIsFancy(e.target.checked) }} /> Use fancy styling </label> </div> ); } function Counter({ isFancy }) { const [score, setScore] = useState(0); const [hover, setHover] = useState(false); let className = 'counter'; if (hover) { className += ' hover'; } if (isFancy) { className += ' fancy'; } return ( <div className={className} onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)} onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)} > <h1>{score}</h1> <button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}> Add one </button> </div> ); }
The counter state gets reset when you click the checkbox. Although you render a Counter, the first child of the div changes from a div to a section. When the child div was removed from the DOM, the whole tree below it (including the Counter and its state) was destroyed as well.
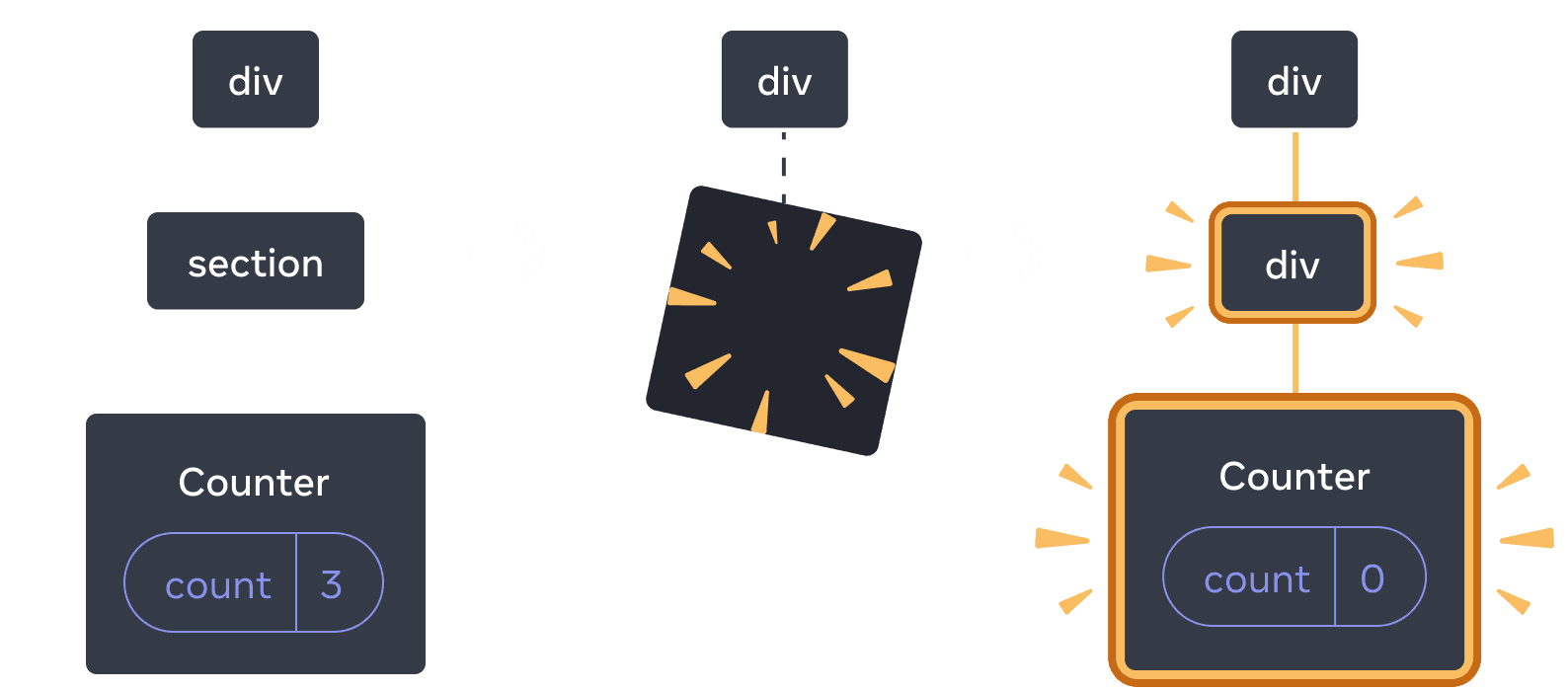
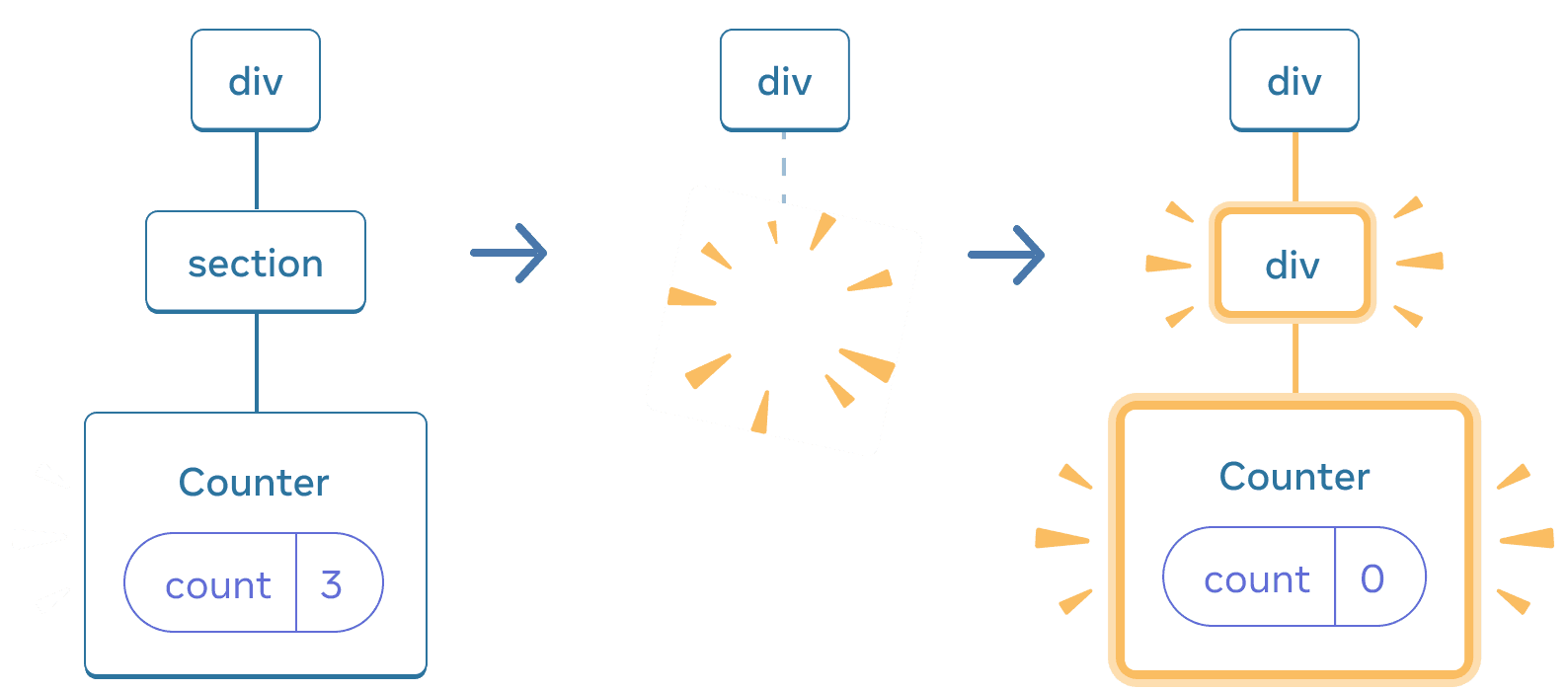
When section changes to div, the section is deleted and the new div is added
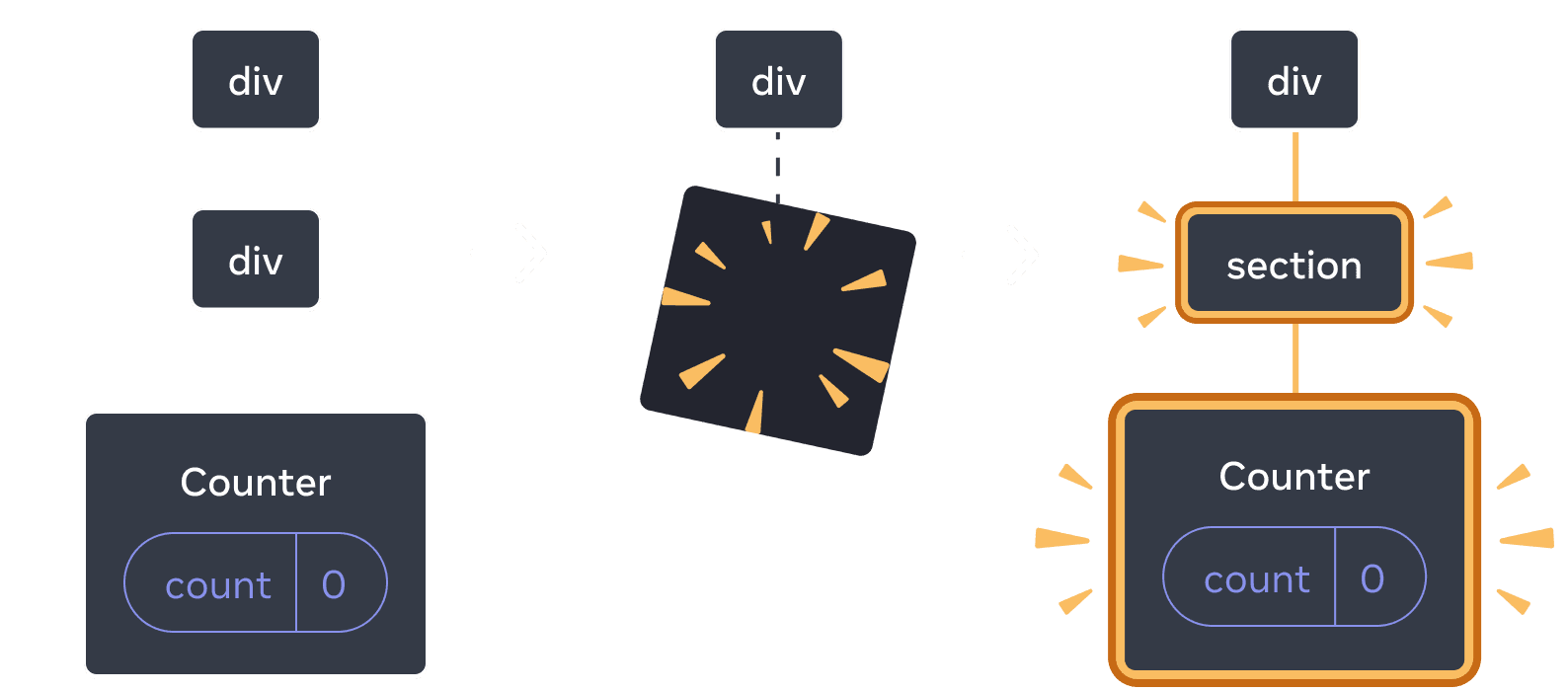
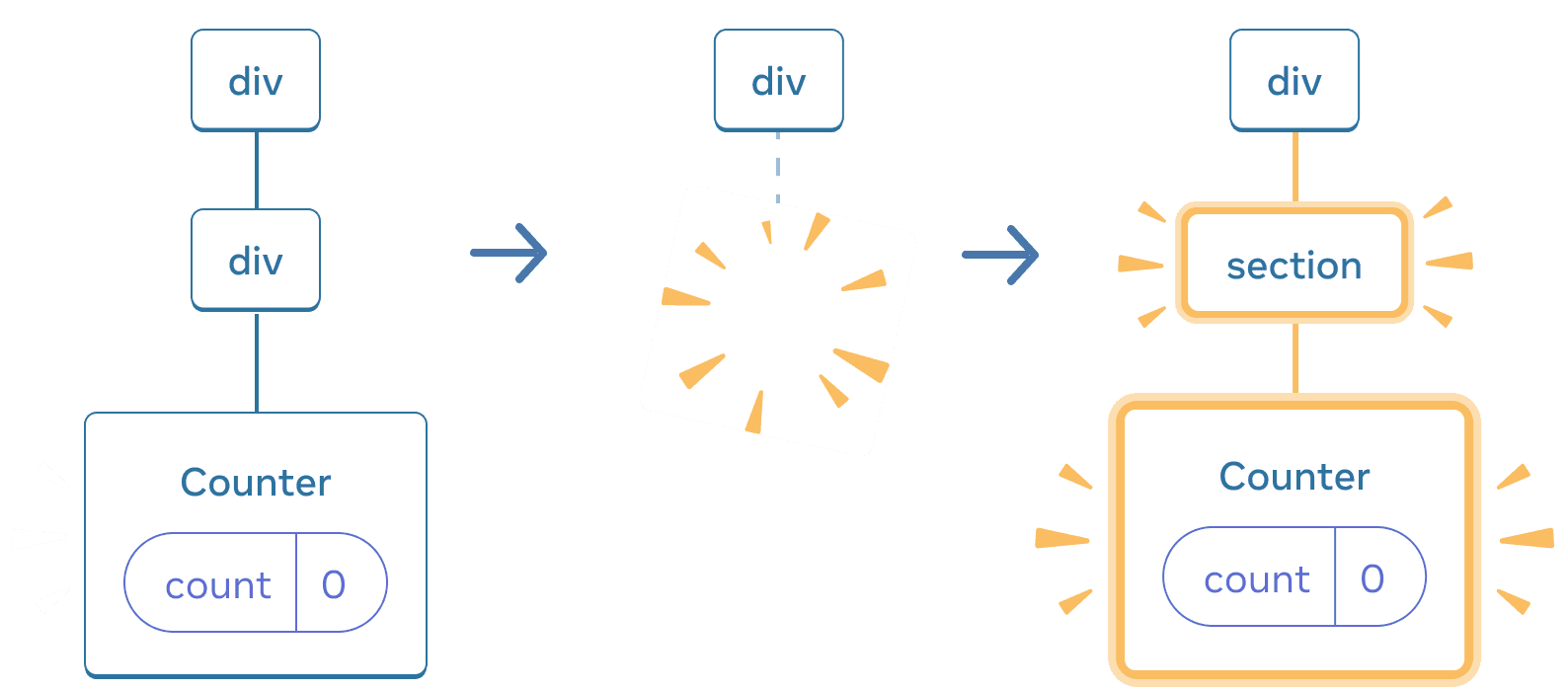
When switching back, the div is deleted and the new section is added
As a rule of thumb, if you want to preserve the state between re-renders, the structure of your tree needs to “match up” from one render to another. If the structure is different, the state gets destroyed because React destroys state when it removes a component from the tree.
Resetting state at the same position
By default, React preserves state of a component while it stays at the same position. Usually, this is exactly what you want, so it makes sense as the default behavior. But sometimes, you may want to reset a component’s state. Consider this app that lets two players keep track of their scores during each turn:
import { useState } from 'react'; export default function Scoreboard() { const [isPlayerA, setIsPlayerA] = useState(true); return ( <div> {isPlayerA ? ( <Counter person="Taylor" /> ) : ( <Counter person="Sarah" /> )} <button onClick={() => { setIsPlayerA(!isPlayerA); }}> Next player! </button> </div> ); } function Counter({ person }) { const [score, setScore] = useState(0); const [hover, setHover] = useState(false); let className = 'counter'; if (hover) { className += ' hover'; } return ( <div className={className} onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)} onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)} > <h1>{person}'s score: {score}</h1> <button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}> Add one </button> </div> ); }
Currently, when you change the player, the score is preserved. The two Counters appear in the same position, so React sees them as the same Counter whose person prop has changed.
But conceptually, in this app they should be two separate counters. They might appear in the same place in the UI, but one is a counter for Taylor, and another is a counter for Sarah.
There are two ways to reset state when switching between them:
- Render components in different positions
- Give each component an explicit identity with
key
Option 1: Rendering a component in different positions
If you want these two Counters to be independent, you can render them in two different positions:
import { useState } from 'react'; export default function Scoreboard() { const [isPlayerA, setIsPlayerA] = useState(true); return ( <div> {isPlayerA && <Counter person="Taylor" /> } {!isPlayerA && <Counter person="Sarah" /> } <button onClick={() => { setIsPlayerA(!isPlayerA); }}> Next player! </button> </div> ); } function Counter({ person }) { const [score, setScore] = useState(0); const [hover, setHover] = useState(false); let className = 'counter'; if (hover) { className += ' hover'; } return ( <div className={className} onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)} onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)} > <h1>{person}'s score: {score}</h1> <button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}> Add one </button> </div> ); }
- Initially,
isPlayerAistrue. So the first position containsCounterstate, and the second one is empty. - When you click the “Next player” button the first position clears but the second one now contains a
Counter.
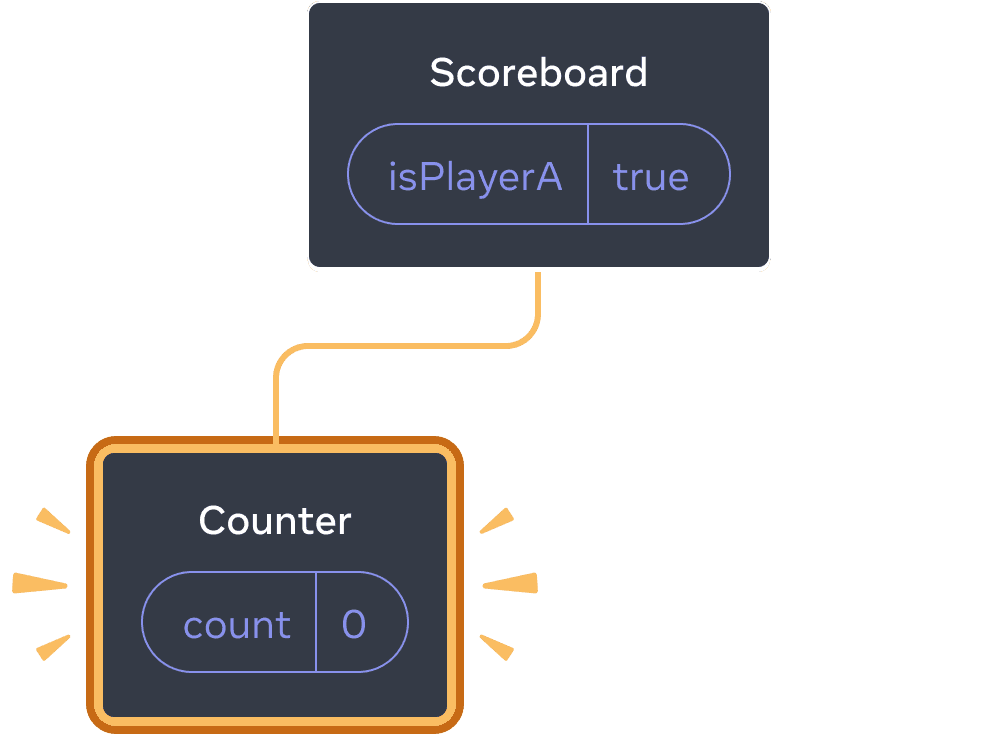
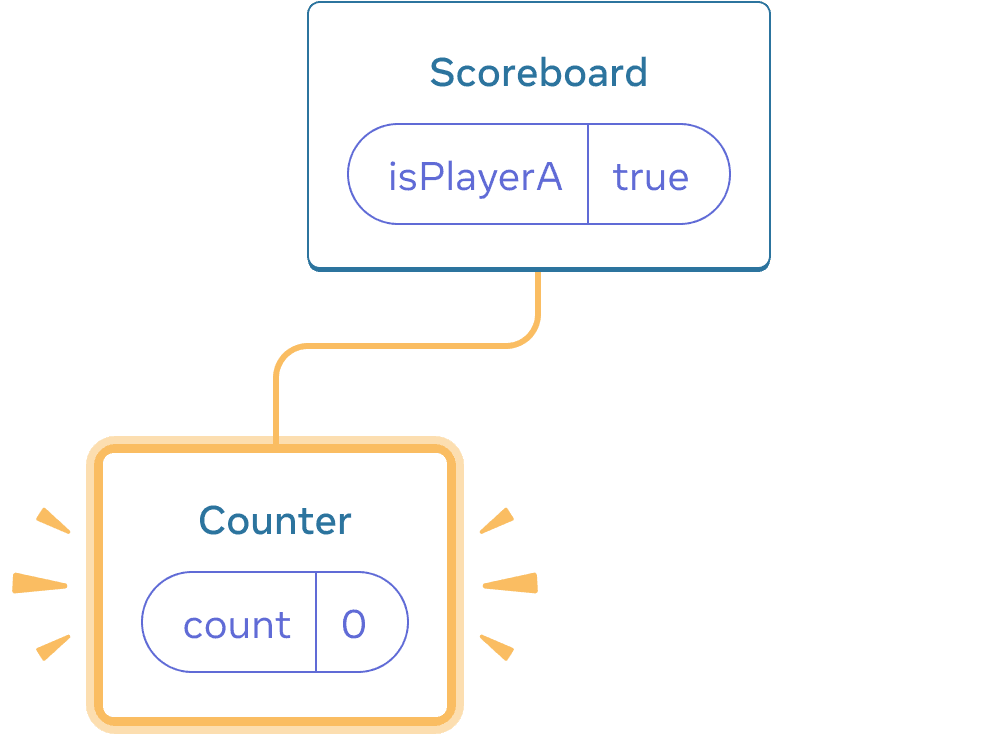
Initial state
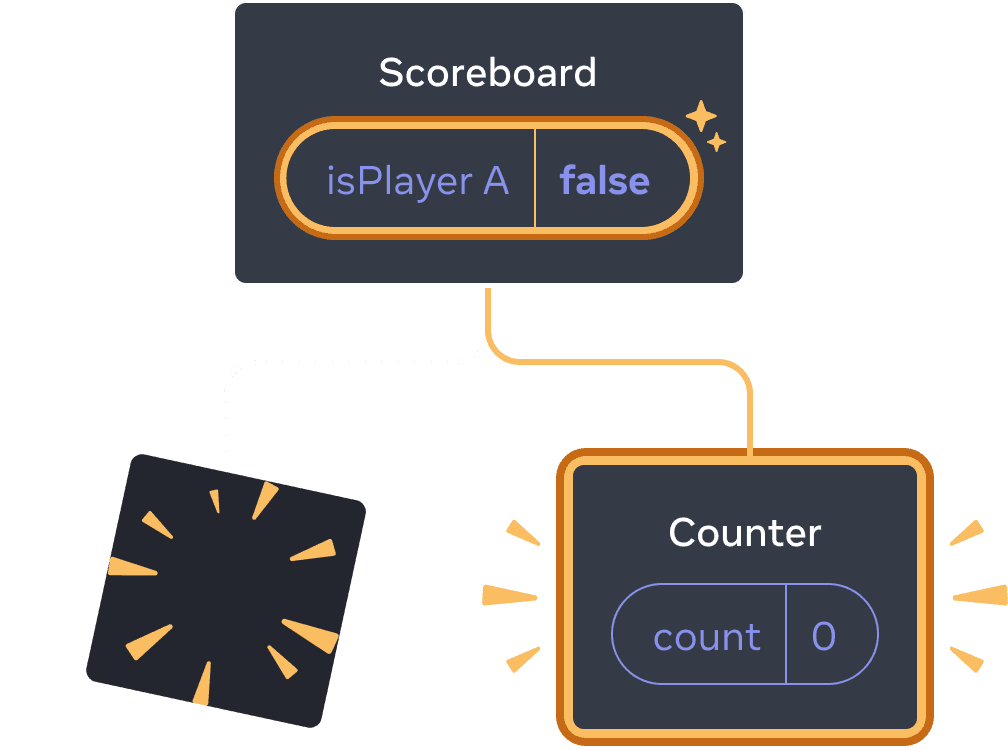
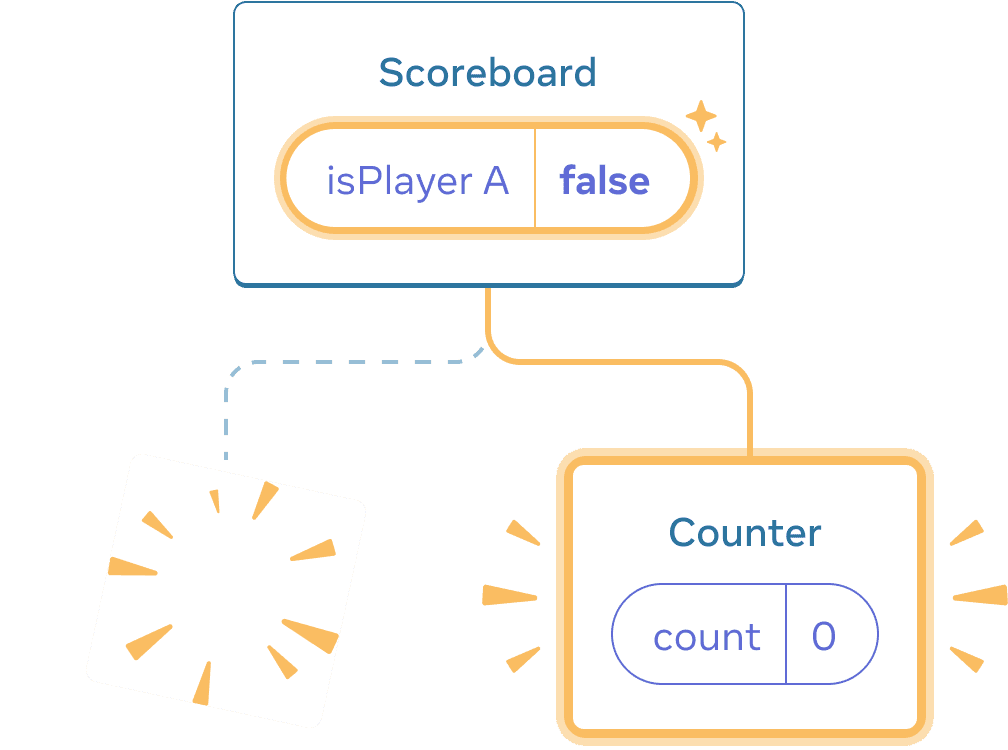
Clicking “next”
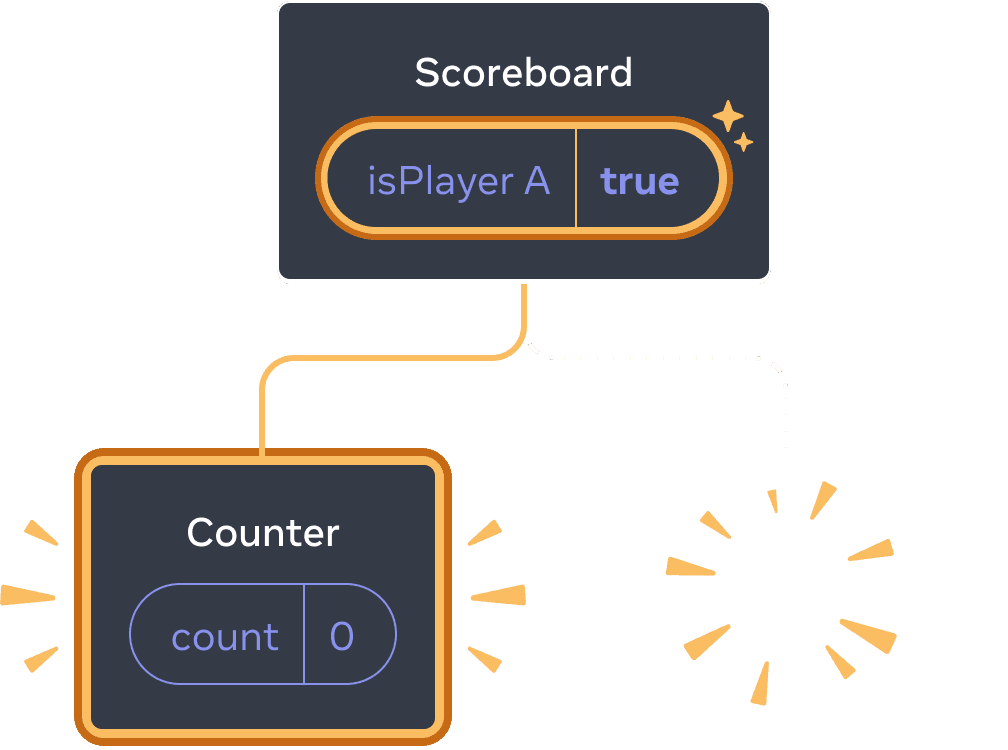
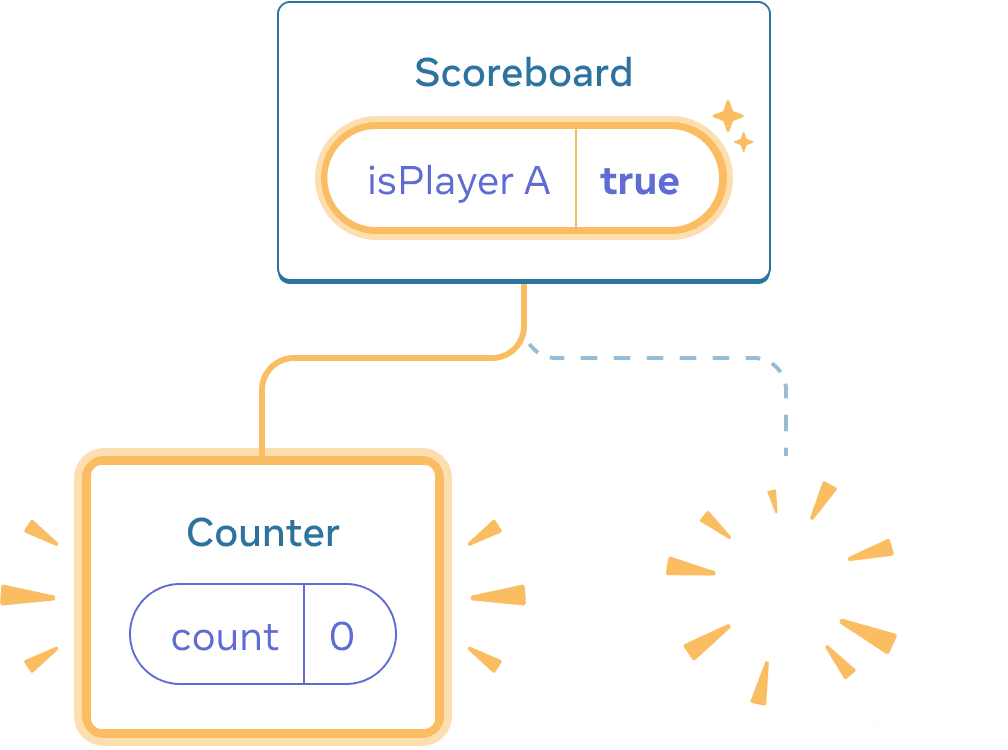
Clicking “next” again
Each Counter’s state gets destroyed each time its removed from the DOM. This is why they reset every time you click the button.
This solution is convenient when you only have a few independent components rendered in the same place. In this example, you only have two, so it’s not a hassle to render both separately in the JSX.
Option 2: Resetting state with a key
There is also another, more generic, way to reset a component’s state.
You might have seen keys when rendering lists. Keys aren’t just for lists! You can use keys to make React distinguish between any components. By default, React uses order within the parent (“first counter”, “second counter”) to discern between components. But keys let you tell React that this is not just a first counter, or a second counter, but a specific counter—for example, Taylor’s counter. This way, React will know Taylor’s counter wherever it appears in the tree!
In this example, the two <Counter />s don’t share state even though they appear in the same place in JSX:
import { useState } from 'react'; export default function Scoreboard() { const [isPlayerA, setIsPlayerA] = useState(true); return ( <div> {isPlayerA ? ( <Counter key="Taylor" person="Taylor" /> ) : ( <Counter key="Sarah" person="Sarah" /> )} <button onClick={() => { setIsPlayerA(!isPlayerA); }}> Next player! </button> </div> ); } function Counter({ person }) { const [score, setScore] = useState(0); const [hover, setHover] = useState(false); let className = 'counter'; if (hover) { className += ' hover'; } return ( <div className={className} onPointerEnter={() => setHover(true)} onPointerLeave={() => setHover(false)} > <h1>{person}'s score: {score}</h1> <button onClick={() => setScore(score + 1)}> Add one </button> </div> ); }
Switching between Taylor and Sarah does not preserve the state. This is because you gave them different keys:
{isPlayerA ? (
<Counter key="Taylor" person="Taylor" />
) : (
<Counter key="Sarah" person="Sarah" />
)}Specifying a key tells React to use the key itself as part of the position, instead of their order within the parent. This is why, even though you render them in the same place in JSX, React sees them as two different counters, and so they will never share state. Every time a counter appears on the screen, its state is created. Every time it is removed, its state is destroyed. Toggling between them resets their state over and over.
Resetting a form with a key
Resetting state with a key is particularly useful when dealing with forms.
In this chat app, the <Chat> component contains the text input state:
import { useState } from 'react'; import Chat from './Chat.js'; import ContactList from './ContactList.js'; export default function Messenger() { const [to, setTo] = useState(contacts[0]); return ( <div> <ContactList contacts={contacts} selectedContact={to} onSelect={contact => setTo(contact)} /> <Chat contact={to} /> </div> ) } const contacts = [ { id: 0, name: 'Taylor', email: 'taylor@mail.com' }, { id: 1, name: 'Alice', email: 'alice@mail.com' }, { id: 2, name: 'Bob', email: 'bob@mail.com' } ];
Try entering something into the input, and then press “Alice” or “Bob” to choose a different recipient. You will notice that the input state is preserved because the <Chat> is rendered at the same position in the tree.
In many apps, this may be the desired behavior, but not in a chat app! You don’t want to let the user send a message they already typed to a wrong person due to an accidental click. To fix it, add a key:
<Chat key={to.id} contact={to} />This ensures that when you select a different recipient, the Chat component will be recreated from scratch, including any state in the tree below it. React will also re-create the DOM elements instead of reusing them.
Now switching the recipient always clears the text field:
import { useState } from 'react'; import Chat from './Chat.js'; import ContactList from './ContactList.js'; export default function Messenger() { const [to, setTo] = useState(contacts[0]); return ( <div> <ContactList contacts={contacts} selectedContact={to} onSelect={contact => setTo(contact)} /> <Chat key={to.id} contact={to} /> </div> ) } const contacts = [ { id: 0, name: 'Taylor', email: 'taylor@mail.com' }, { id: 1, name: 'Alice', email: 'alice@mail.com' }, { id: 2, name: 'Bob', email: 'bob@mail.com' } ];
Köfum dýpra
In a real chat app, you’d probably want to recover the input state when the user selects the previous recipient again. There are a few ways to keep the state “alive” for a component that’s no longer visible:
- You could render all chats instead of just the current one, but hide all the others with CSS. The chats would not get removed from the tree, so their local state would be preserved. This solution works great for simple UIs. But it can get very slow if the hidden trees are large and contain a lot of DOM nodes.
- You could lift the state up and hold the pending message for each recipient in the parent component. This way, when the child components get removed, it doesn’t matter, because it’s the parent that keeps the important information. This is the most common solution.
- You might also use a different source in addition to React state. For example, you probably want a message draft to persist even if the user accidentally closes the page. To implement this, you could have the
Chatcomponent initialize its state by reading from thelocalStorage, and save the drafts there too.
No matter which strategy you pick, a chat with Alice is conceptually distinct from a chat with Bob, so it makes sense to give a key to the <Chat> tree based on the current recipient.
Recap
- React keeps state for as long as the same component is rendered at the same position.
- State is not kept in JSX tags. It’s associated with the tree position in which you put that JSX.
- You can force a subtree to reset its state by giving it a different key.
- Don’t nest component definitions, or you’ll reset state by accident.
Challenge 1 of 5: Fix disappearing input text
This example shows a message when you press the button. However, pressing the button also accidentally resets the input. Why does this happen? Fix it so that pressing the button does not reset the input text.
import { useState } from 'react'; export default function App() { const [showHint, setShowHint] = useState(false); if (showHint) { return ( <div> <p><i>Hint: Your favorite city?</i></p> <Form /> <button onClick={() => { setShowHint(false); }}>Hide hint</button> </div> ); } return ( <div> <Form /> <button onClick={() => { setShowHint(true); }}>Show hint</button> </div> ); } function Form() { const [text, setText] = useState(''); return ( <textarea value={text} onChange={e => setText(e.target.value)} /> ); }